|
|
 |
 CHARACTERISTICS
REFERENCE/TEMPERATURE
CHARACTERISTICS
REFERENCE/TEMPERATURE |
| CHARACTERISTICS
REFERENCE |
|
GENERAL APPLICATION REFERENCE |
Plastic film capacitors are now widely
used by the electronic industry, and their selection is based upon
the following factors:
|
-
FREQUENCY :
Polyester (PE) capacitors have higher dielectric losses and as are
generally suitable at frequencies of 10KHz or less. They have a
wider temperature range than the other common use dielectric
materials and due to a higher dielectric constant can produce
high C values in smaller package dimensions.
Polypropylene (PP) capacitors have relatively low dissipation
factors and dielectric losses, as such they are suitable for
high voltages, high frequencies and high pulse current. They are
larger in size, have a narrow temperature range and negative
temperature coefficient.
Polycarbonate (PC) capacitors have moderate features of both PE & PP
styles, but are more expensive. They do and more stable
capacitance versus temperature characteristics and good long
term stability.
Polystyrene (PS) capacitors have excellent high frequency
performance due to their low dissipation factor and very low
dielectric absorption characteristics.
- PEAK
VOLTAGE :
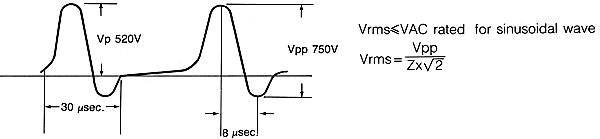
The peak voltage against a zero potential reference shall always be
less than nominal DC voltage rating of the capacitor.
The rate of voltage change (div/DT) of individual specification are
valid for pulse voltage equal to or less than the rated DC
voltage. If the pulse voltage is less, then a factor of
"VDU/applied" may be used.
Vp< = VDC rated
and the Vrms voltage dervied from the peak voltage shall always be
less than the nominal AC voltage rating of the capacitor.
-
PERMISSIBLE CURRENT :
Under AC operation, the permissible current to capacitor must be
less than Ap-p. As the following details and graphs indicate,
operation at higher than permissible currents may deteriorate
performance and damage the capacitor due to internal temperature
rise.
-
INHERENT TEMPERATURE RISE :
When capacitor is operated in AC circuit, especially at high
frequency, temperature of capacitor rises inherently In case
temperature rises too high, performance of capacitor may be
deteriorated or damaged. The inherent temperature rise at no air
circulation (Ambient. at 40°C) shall be within a value specified
below. (The allowable value depends on dielectric. For details,
consult our office or sales representative.)
|
 |
|

